Three Layer Achitecture in C#.NET
First let me give you small overview about topic I would like to cover in this artical.
1. Tier vs. Layer
2. Three Tier/Layer Architecture Design Components
3. Demo: Three Layer Windows Application in C#.NET
1. Tier vs. Layer
1.1 Tier: Tier indicates a physical separation of components, which may mean different assemblies such as DLL, EXE etc on the same server or multiple servers.
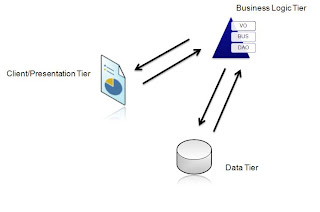
As you can see in the above figure Data Tier have no direction with Presentation Tier, but there is intermediate Tire called Business Tier which is mainly responsible to pass the data from Data Tier to Presentation Tier and to add defined business logic to Data.
So, If we seperete each Tier by their funcationality then we come to know on below conclusion

1.2 Layer: Layer indicates logical separation of components, such as having distinct namespaces and classes for the Database Access Layer, Business Logic Layer and User Interface Layer.

2. Three Tier/Layer Architecture Design Components
As we already seen tier is sum of all the physical components, we can separate the three tiers as Data Tier, Business Tier and Presentation Tier.

- Data Tier is basically the server which stores all the application’s data. Data tier contents Database Tables, XML Files and Other means of storing Application Data.
- Business Tier is the mainly working as bridge between Data Tier and Presentation Tier. All the Data is parsing through Business Tier before parsing to presentation Tier. Business Tier is sum of Business Logic Layer, Data Access Layer and Value Object and other components used to add business logic.
- Presentation Tier is the tier in which user’s interact with an application. Presentation Tier contents Shared UI code, Code Behind and Designers used to represent information to user.

Above figure is a mixture of Three Tier and Three Layer Architecture. Here, we can clearly see a differen between Tier and Layer. Since each components are independent of each other, they are easily maintable without changing to whole code.
This approach is really very important when several developer are work on same project and some module need to re-use in other project. In a way we can distribue a work among developer and also maintain it in future without much problem in future.
Testing is also a very important issue for Arhitecture when we are considering writing a testcase for the project. Since it’s like a modular architecture it’s very handy testing each module and to trace out bug without going to whole code.
3. Demo: 3 Layer Windows Application in C#.NET

Let’s go thought from each module to other to have better understanding of it.
dbConnection:
This class is mainly use to do the database activity like Select, Update and Delete query to database. It also checks if the database connection is open or not. If database connection is not open then it opens the connection and performs the database query. The database results are to be receive and being pass in Data Table in this class.
This class takes the database setting from the app.config file so it’s really flexible to manage the database settings.
—
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Data;
using System.Data.SqlClient;
using System.Configuration;
namespace ThreeLayerDemo.Core
{
public class dbConnection
{
private SqlCommand myCommand;
private SqlDataAdapter myAdapter;
private SqlConnection conn;
///
/// Initialise Connection
///
public dbConnection()
{
myCommand = new SqlCommand();
myAdapter = new SqlDataAdapter();
conn = new SqlConnection(ConfigurationManager.ConnectionStrings"dbConnectionString"].ConnectionString);
try
{
myCommand.Connection = openConnection();
}
catch
{
Console.Write("Error - constructor.dbConnection");
}
}
///
/// Open Database Connection if Closed or Broken
///
private SqlConnection openConnection()
{
if (conn.State == ConnectionState.Closed || conn.State == ConnectionState.Broken)
{
conn.Open();
}
return conn;
}
///
/// Select Query
///
public DataTable executeSelectQuery(String _query)
{
DataTable dataTable = new DataTable();
dataTable = null;
DataSet ds = new DataSet();
try
{
myCommand.Connection = openConnection();
myCommand.CommandText = _query;
myCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
myAdapter.SelectCommand = myCommand;
myAdapter.Fill(ds);
dataTable = ds.Tables[0];
}
catch (SqlException e)
{
Console.Write("Error - Connection.executeSelectQuery - Query: " + _query + " \nException: " + e.StackTrace.ToString());
return null;
}
finally
{
}
return dataTable;
}
///
/// Insert Query
///
public bool executeInsertQuery(String _query)
{
try
{
myCommand.Connection = openConnection();
myCommand.CommandText = _query;
myAdapter.InsertCommand = myCommand;
myCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
catch (SqlException e)
{
Console.Write("Error - Connection.executeInsertQuery - Query: " + _query + " \nException: \n" + e.StackTrace.ToString());
return false;
}
finally
{
}
return true;
}
///
/// Update Query
///
public bool executeUpdateQuery(String _query)
{
try
{
myCommand.Connection = openConnection();
myCommand.CommandText = _query;
myAdapter.UpdateCommand = myCommand;
myCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
catch (SqlException e)
{
Console.Write("Error - Connection.executeUpdateQuery - Query: " + _query + " \nException: " + e.StackTrace.ToString());
return false;
}
finally
{
}
return true;
}
}
}
Database Access Layer:
Database Access Layer (DAO) builds the query based on received parameters from the Business Logic Layer and passes it the dbConnection class for execution. And simple return results from the dbConnection class to Business Logic Layer.
---
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Data;
namespace ThreeLayerDemo.Core
{
public class UserDAO
{
private dbConnection conn;
///
/// Constructor UserDAO
///
public UserDAO()
{
conn = new dbConnection();
}
///
/// Get User Email By Firstname or Lastname and return DalaTable
///
public DataTable searchByName(string _username)
{
string query = "select * from [t01_user] where t01_firstname like '" + _username + "' or t01_lastname like '" + _username + "' ";
return conn.executeSelectQuery(query);
}
///
/// Get User Email By Id and return DalaTable
///
public DataTable searchById(string _id)
{
string query = "select * from [t01_user] where t01_id = '" + _id + "' "; return conn.executeSelectQuery(query);
}
}
}
Value Object:
Value Object is nothing more but class which contents GET and SET methods. It’s mainly use to pass Data from one class to other. It’s directly connected with Business Logic Layer and Presentation Layer. As you can see in the diagram object value are being SET in Business Logic Layer and GET from Presentation Layer.
---
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;using System.Text;
namespace ThreeLayerDemo.Core
{
public class UserVO
{
private int _idUser;
private string _firstname;
private string _lastname;
private string _email;
///
/// Constructor UserVO
///
public UserVO()
{
//
// TODO: Add constructor logic here
//
}
public int idUser
{
get
{
return _idUser;
}
set
{
_idUser = value;
}
}
public string firstname
{
get
{
return _firstname;
}
set
{
_firstname = value;
}
}
public string lastname
{
get
{
return _lastname;
}
set
{
_lastname = value;
}
}
public string email
{
get
{
return _email;
}
set
{
_email = value;
}
}
}
}
Business Logic Layer:
Business Logic Layer (BUS) works as a bridge between Presentation Layer and DAO. All the user value received from the presentation layer and being passed to BUS. The results received from the DAO are in row data in Data Table format but in BUS it’s converting into Value Objects (VO). Business Logic Layer (BUS) is most important class in the whole architecture because it mainly contents all the business logic of the program. Whenever user wants to update the business logic of the program only need to update this class.
---
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;using System.Text;
using System.Data;
namespace ThreeLayerDemo.Core
{
///
/// Summary description for UserBUS
///
public class UserBUS
{
private UserDAO _userDAO;
///
/// Constructor UserBUS
///
public UserBUS()
{
_userDAO = new UserDAO();
}
///
/// Get User Email By Firstname or Lastname and return VO
///
public UserVO getUserEmailByName(string name)
{
UserVO userVO = new UserVO();
DataTable dataTable = new DataTable();
dataTable = _userDAO.searchByName(name);
foreach (DataRow dr in dataTable.Rows)
{
userVO.idUser = Int32.Parse(dr["t01_id"].ToString());
userVO.firstname = dr["t01_firstname"].ToString();
userVO.lastname = dr["t01_lastname"].ToString();
userVO.email = dr["t01_email"].ToString();
}
return userVO;
}
///
/// Get User Email By Id and return DalaTable
///
public UserVO getUserById(string _id)
{
UserVO userVO = new UserVO();
DataTable dataTable = new DataTable();
dataTable = _userDAO.searchById(_id);
foreach (DataRow dr in dataTable.Rows)
{
userVO.idUser = Int32.Parse(dr["t01_id"].ToString());
userVO.firstname = dr["t01_firstname"].ToString();
userVO.lastname = dr["t01_lastname"].ToString();
userVO.email = dr["t01_email"].ToString();
}
return userVO;
}
}
}
Presentation Layer:
Presentation Layer is the only layer which is directly connected with the user. So in this matter it’s also really important layer for the marketing purpose. Presentation Layer is mainly used for getting user data and then passing it to Business Logic Layer for further procedure, and when data received in Value Object then it’s responsible to represent value object in the appropriate form which user can understand.
---
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using ThreeLayerDemo.Core;
namespace ThreeLayerDemo
{
public partial class frmLogin : Form
{
private UserBUS _userBUS;
public frmLogin()
{
InitializeComponent();
_userBUS = new UserBUS();
}
private void btnSearch_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
UserVO _userVO = new UserVO();
_userVO = _userBUS.getUserEmailByName(txtUsername.Text);
MessageBox.Show(_userVO.email ,"Result",MessageBoxButtons.OK,MessageBoxIcon.Exclamation);
}
private void btnCancel_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Close();
}
}
}
1. Tier vs. Layer
2. Three Tier/Layer Architecture Design Components
3. Demo: Three Layer Windows Application in C#.NET
1. Tier vs. Layer
1.1 Tier: Tier indicates a physical separation of components, which may mean different assemblies such as DLL, EXE etc on the same server or multiple servers.

As you can see in the above figure Data Tier have no direction with Presentation Tier, but there is intermediate Tire called Business Tier which is mainly responsible to pass the data from Data Tier to Presentation Tier and to add defined business logic to Data.
So, If we seperete each Tier by their funcationality then we come to know on below conclusion

1.2 Layer: Layer indicates logical separation of components, such as having distinct namespaces and classes for the Database Access Layer, Business Logic Layer and User Interface Layer.

2. Three Tier/Layer Architecture Design Components
As we already seen tier is sum of all the physical components, we can separate the three tiers as Data Tier, Business Tier and Presentation Tier.

- Data Tier is basically the server which stores all the application’s data. Data tier contents Database Tables, XML Files and Other means of storing Application Data.
- Business Tier is the mainly working as bridge between Data Tier and Presentation Tier. All the Data is parsing through Business Tier before parsing to presentation Tier. Business Tier is sum of Business Logic Layer, Data Access Layer and Value Object and other components used to add business logic.
- Presentation Tier is the tier in which user’s interact with an application. Presentation Tier contents Shared UI code, Code Behind and Designers used to represent information to user.

Above figure is a mixture of Three Tier and Three Layer Architecture. Here, we can clearly see a differen between Tier and Layer. Since each components are independent of each other, they are easily maintable without changing to whole code.
This approach is really very important when several developer are work on same project and some module need to re-use in other project. In a way we can distribue a work among developer and also maintain it in future without much problem in future.
Testing is also a very important issue for Arhitecture when we are considering writing a testcase for the project. Since it’s like a modular architecture it’s very handy testing each module and to trace out bug without going to whole code.
3. Demo: 3 Layer Windows Application in C#.NET

Let’s go thought from each module to other to have better understanding of it.
dbConnection:
This class is mainly use to do the database activity like Select, Update and Delete query to database. It also checks if the database connection is open or not. If database connection is not open then it opens the connection and performs the database query. The database results are to be receive and being pass in Data Table in this class.
This class takes the database setting from the app.config file so it’s really flexible to manage the database settings.
—
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Data;
using System.Data.SqlClient;
using System.Configuration;
namespace ThreeLayerDemo.Core
{
public class dbConnection
{
private SqlCommand myCommand;
private SqlDataAdapter myAdapter;
private SqlConnection conn;
///
/// Initialise Connection
///
public dbConnection()
{
myCommand = new SqlCommand();
myAdapter = new SqlDataAdapter();
conn = new SqlConnection(ConfigurationManager.ConnectionStrings"dbConnectionString"].ConnectionString);
try
{
myCommand.Connection = openConnection();
}
catch
{
Console.Write("Error - constructor.dbConnection");
}
}
///
/// Open Database Connection if Closed or Broken
///
private SqlConnection openConnection()
{
if (conn.State == ConnectionState.Closed || conn.State == ConnectionState.Broken)
{
conn.Open();
}
return conn;
}
///
/// Select Query
///
public DataTable executeSelectQuery(String _query)
{
DataTable dataTable = new DataTable();
dataTable = null;
DataSet ds = new DataSet();
try
{
myCommand.Connection = openConnection();
myCommand.CommandText = _query;
myCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
myAdapter.SelectCommand = myCommand;
myAdapter.Fill(ds);
dataTable = ds.Tables[0];
}
catch (SqlException e)
{
Console.Write("Error - Connection.executeSelectQuery - Query: " + _query + " \nException: " + e.StackTrace.ToString());
return null;
}
finally
{
}
return dataTable;
}
///
/// Insert Query
///
public bool executeInsertQuery(String _query)
{
try
{
myCommand.Connection = openConnection();
myCommand.CommandText = _query;
myAdapter.InsertCommand = myCommand;
myCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
catch (SqlException e)
{
Console.Write("Error - Connection.executeInsertQuery - Query: " + _query + " \nException: \n" + e.StackTrace.ToString());
return false;
}
finally
{
}
return true;
}
///
/// Update Query
///
public bool executeUpdateQuery(String _query)
{
try
{
myCommand.Connection = openConnection();
myCommand.CommandText = _query;
myAdapter.UpdateCommand = myCommand;
myCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
catch (SqlException e)
{
Console.Write("Error - Connection.executeUpdateQuery - Query: " + _query + " \nException: " + e.StackTrace.ToString());
return false;
}
finally
{
}
return true;
}
}
}
Database Access Layer:
Database Access Layer (DAO) builds the query based on received parameters from the Business Logic Layer and passes it the dbConnection class for execution. And simple return results from the dbConnection class to Business Logic Layer.
---
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Data;
namespace ThreeLayerDemo.Core
{
public class UserDAO
{
private dbConnection conn;
///
/// Constructor UserDAO
///
public UserDAO()
{
conn = new dbConnection();
}
///
/// Get User Email By Firstname or Lastname and return DalaTable
///
public DataTable searchByName(string _username)
{
string query = "select * from [t01_user] where t01_firstname like '" + _username + "' or t01_lastname like '" + _username + "' ";
return conn.executeSelectQuery(query);
}
///
/// Get User Email By Id and return DalaTable
///
public DataTable searchById(string _id)
{
string query = "select * from [t01_user] where t01_id = '" + _id + "' "; return conn.executeSelectQuery(query);
}
}
}
Value Object:
Value Object is nothing more but class which contents GET and SET methods. It’s mainly use to pass Data from one class to other. It’s directly connected with Business Logic Layer and Presentation Layer. As you can see in the diagram object value are being SET in Business Logic Layer and GET from Presentation Layer.
---
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;using System.Text;
namespace ThreeLayerDemo.Core
{
public class UserVO
{
private int _idUser;
private string _firstname;
private string _lastname;
private string _email;
///
/// Constructor UserVO
///
public UserVO()
{
//
// TODO: Add constructor logic here
//
}
public int idUser
{
get
{
return _idUser;
}
set
{
_idUser = value;
}
}
public string firstname
{
get
{
return _firstname;
}
set
{
_firstname = value;
}
}
public string lastname
{
get
{
return _lastname;
}
set
{
_lastname = value;
}
}
public string email
{
get
{
return _email;
}
set
{
_email = value;
}
}
}
}
Business Logic Layer:
Business Logic Layer (BUS) works as a bridge between Presentation Layer and DAO. All the user value received from the presentation layer and being passed to BUS. The results received from the DAO are in row data in Data Table format but in BUS it’s converting into Value Objects (VO). Business Logic Layer (BUS) is most important class in the whole architecture because it mainly contents all the business logic of the program. Whenever user wants to update the business logic of the program only need to update this class.
---
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;using System.Text;
using System.Data;
namespace ThreeLayerDemo.Core
{
///
/// Summary description for UserBUS
///
public class UserBUS
{
private UserDAO _userDAO;
///
/// Constructor UserBUS
///
public UserBUS()
{
_userDAO = new UserDAO();
}
///
/// Get User Email By Firstname or Lastname and return VO
///
public UserVO getUserEmailByName(string name)
{
UserVO userVO = new UserVO();
DataTable dataTable = new DataTable();
dataTable = _userDAO.searchByName(name);
foreach (DataRow dr in dataTable.Rows)
{
userVO.idUser = Int32.Parse(dr["t01_id"].ToString());
userVO.firstname = dr["t01_firstname"].ToString();
userVO.lastname = dr["t01_lastname"].ToString();
userVO.email = dr["t01_email"].ToString();
}
return userVO;
}
///
/// Get User Email By Id and return DalaTable
///
public UserVO getUserById(string _id)
{
UserVO userVO = new UserVO();
DataTable dataTable = new DataTable();
dataTable = _userDAO.searchById(_id);
foreach (DataRow dr in dataTable.Rows)
{
userVO.idUser = Int32.Parse(dr["t01_id"].ToString());
userVO.firstname = dr["t01_firstname"].ToString();
userVO.lastname = dr["t01_lastname"].ToString();
userVO.email = dr["t01_email"].ToString();
}
return userVO;
}
}
}
Presentation Layer:
Presentation Layer is the only layer which is directly connected with the user. So in this matter it’s also really important layer for the marketing purpose. Presentation Layer is mainly used for getting user data and then passing it to Business Logic Layer for further procedure, and when data received in Value Object then it’s responsible to represent value object in the appropriate form which user can understand.
---
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using ThreeLayerDemo.Core;
namespace ThreeLayerDemo
{
public partial class frmLogin : Form
{
private UserBUS _userBUS;
public frmLogin()
{
InitializeComponent();
_userBUS = new UserBUS();
}
private void btnSearch_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
UserVO _userVO = new UserVO();
_userVO = _userBUS.getUserEmailByName(txtUsername.Text);
MessageBox.Show(_userVO.email ,"Result",MessageBoxButtons.OK,MessageBoxIcon.Exclamation);
}
private void btnCancel_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Close();
}
}
}
Comments
Post a Comment